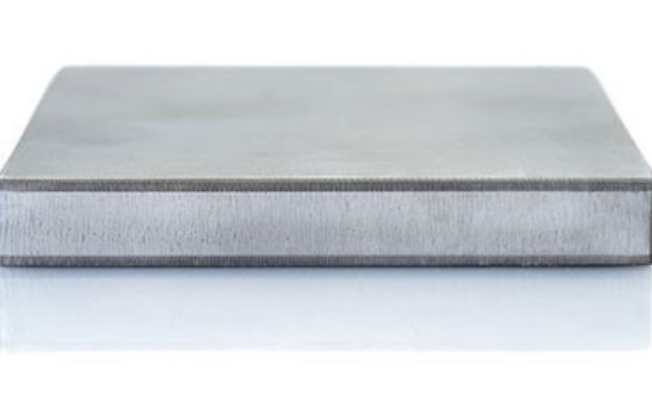
What Is 316 Stainless Steel Clad Plate?
316 Stainless clad steel plate is classified as a composite steel that is created by bonding two or more metals together. Typically, the base material includes low alloy steel and carbon steel, and the cladding material is stainless steel. The plate combines the necessary strength of a structural material (base metal) with the resistance to heat and corrosion (cladding material). Moreover, it offers substantial economic benefits because the plate is lower in cost than similar products made entirely of cladding material. Consequently, it is extensively used in a variety of industrial fields and sectors.

316 SS Cladding Plate Specifications
| Raw Material | base metal: low alloy steel or carbon steel (Q235B、Q345R、Q355、Q245R、20#、40#…)
cladding metal: stainless steel (304, 304L, 310, 310S, 316, 321, 318, 410S, 420, 904L…) |
| Grade | 316 |
| Standard | ASTM, AISI, DIN, EN, GB, JIS |
| Thickness | base material thickness: 0.5 – 50 mm
cladding material thickness: 1.5 – 20 mm cladding thickness: 1.5 – 5 mm |
| Width | 100 – 800 mm |
| Length | 500 – 15000 mm |
| Shape | rectangular, square, round, or as required |
| Production Method | explosive cladding, hot/cold rolling |
| Surface | NO.1, 2B, BA, 4K, 8K, HL, NO.4, annealed, pickled, polished, |
| Processing Services | cutting, shearing, welding, leveling, rolling, punching, bending, etc |
| Package | standard export seaworthy package or as required |
Additional stainless steel cladding design considerations include:
1. The thickness of the cladding is typically in the range of 1.5 to 5 mm. The cladding thickness of higher than 5mm is possible and the cladding thickness of less than 1.5 mm is difficult.
2. The cladding thickness of explosive bonding ranges from 1.5 mm to 2.5 mm.
3. The thickness of the clad layer should be at least half the thickness of the base metal. For most purposes, the recommended thickness for stainless steel cladding on carbon steel is 3 mm.
4. The material and thickness can be freely combined to meet the needs of different users.
How Is It Manufactured?
Cladding is a technique in which two dissimilar metals are bonded together by mechanical equipment under high pressure. When producing 316 stainless clad plates, there are often two ways to employ: explosion and rolling bonding.
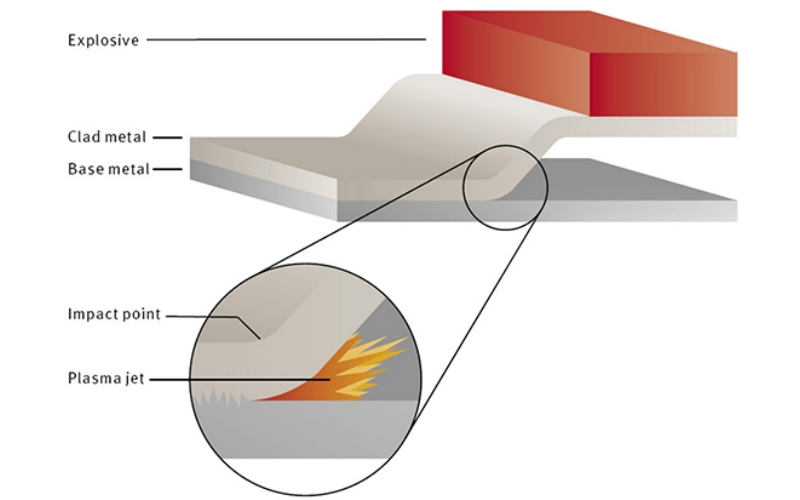
1. Explosive Bonding
Explosion bonding is a solid-state joining process in which explosive energy is used to propel the two metals together to form a metallurgical bond. Here are some concrete steps you can see:
1. Prepare the base steel and cladding steel.
2. Lay a layer of explosives on the cladding material.
3. Dynamite exploded. It will make the stainless steel plate hit the carbon steel substrate at high speed, generating high temperature and high pressure to realize solid phase welding at the interface of the two materials. Under ideal conditions, the shear strength per square millimeter of the interface can reach 400 MPa.
Sometimes, explosive bonding will be followed by the hot rolling process to further improve the bond between carbon steel and stainless steel.
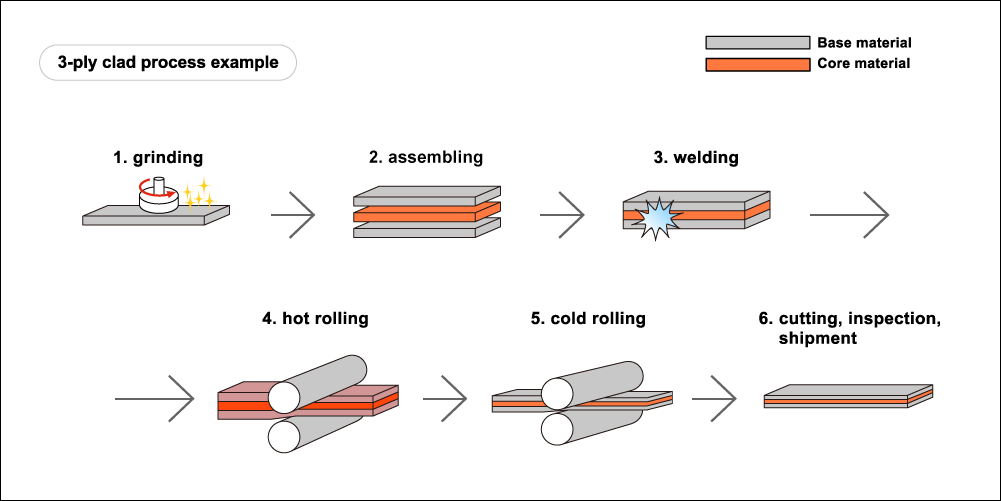
2. Rolling Bonding
The standard method of producing this clad steel is by rolling cladding method, including hot rolling and cold rolling.
Hot Rolling: it is a commonly used method. In this process, the clean plates of carbon steel and stainless steel are placed on each other (single-side cladding), or sandwiched between two stainless steel plates (double-side cladding). The composite plates then are hot rolled together through a conventional hot rolling mill. Finally, a metallurgical bond will form between carbon steel and stainless steel during heating and rolling.
Cold Rolling: when the hot rolled stainless steel clad plate is cooled down, it will go through some procedures like annealing, pickling, cold rolling, intermediate annealing, pickling, tension leveling, and other production processes. These are the production method of cold-rolled 316 stainless steel clad plates. Compared with the former, it has a much more precise size, brighter surface, and higher strength. Besides, the thinnest thickness of this type can achieve 0.6 mm.
Features and Advantages
316 Stainless clad steel plate offers a highly effective solution in different industrial sectors. Further advantages of it include:
1. Excellent Corrosion Resistance
The chromium, nickel, and molybdenum content in 316 stainless steel provides increased resistance to corrosion and rust to extend its operational life. It can protect the structure from attack by temperature, wind, water absorption, sunlight, pollution, organic acids, and other strong media. Also, its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion further enhances its suitability, especially in chloride-rich environments.
2. Excellent Bonding Characteristic
By special technology, the composite interface of these two materials can achieve good and firm metallurgical bonding. And the interface strength is very high.
3. Long Lifespan
Stainless steel cladding will sustain itself for years, without the need for repair or renovation. Comparatively speaking, it has a longer lifespan than other cladding materials, about 50 years.
4. Polished Finish
This kind of plate usually has a smooth, bright, and non-porous surface, helpful to add extra aesthetic value to your projects. If needed, a simple clean can be used to retain and maintain its beautiful properties within a project.
5. Good Processing Performance
Like other steel materials, it can also perform various processing such as hot forming, cold bending, cutting, welding, drawing, etc., and has good process performance. However, it is incredibly difficult to punch, drill, or machine.
6. Low-cost Solution
316 Stainless steel cladding plate is a highly efficient and green material. On one hand, compared with stainless steel plates, it can reduce alloy elements like chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni) by 70–80 %, and reduce costs by 30–50 % because of the low cost of carbon steel. On the other hand, it has achieved the effect of saving resources and reducing costs without reducing the use effect (anti-corrosion performance, mechanical strength, toughness, etc).

Applications and Uses
316 Stainless steel cladding materials offer immense benefits to heavy and light industries. Examples of clad plate applications include:
1. Construction: building material, marine protection projects, architectural improvement, shipbuilding, steel structures, roofing panels, desalination plant, etc.
2. Manufacturing: use as the main substrate for making stainless steel products in coils, pipes, coils, wires, profiles, fittings, etc. Others include heavy-duty tanks, pressure vessel fabrication, industrial scrubbers, chemical storage, food processing, upgrade of coking equipment, material-handling equipment, pharmaceutical equipment, etc.
3. Industry: used to make pressure vessels, pagodas, conveyor systems, pumps, water treatment plants, steam boilers, burners, and other industrial equipment.
4. Public uses: reactors, heat exchangers, separators, cookwares, elevators, agricultural projects, water conservancy, electronics, home appliances, and other decoration projects.


Selecting 316 Stainless Clad Plates for Your Projects
Ultimately, stainless steel cladding design is a smart and sustainable choice for a wide range of construction projects. It achieves the perfect combination of low cost and high performance, with good social benefits. Looking for it? Gnee Steel has the largest range in stock now.
Gnee Steel is an expert in the manufacture of high-performance and cost-effective stainless steel composite panels for more than 15 years. Depending upon your specific demands, the plate is available in different textures, colors, designs, shapes, and sizes. Contact us today for a free quote or to find out more about the different stainless steel products.


