What is a Stainless Steel Pipe?
A stainless steel pipe is defined as a tubular product made by transforming stainless steel into a hollow cylindrical shape. It is typically manufactured using either seamless or welded techniques.
Seamless pipes are formed without any welding joints through the extrusion or rotary piercing process. On the other hand, welded pipes are produced by joining two edges of stainless steel plates or coils using different welding methods.

Stainless Steel Pipes Are Useful and Versatile in a Variety of Industries
Firstly, the corrosion resistance exhibited by stainless steel pipes ensures longevity and reliability in harsh environments exposed to moisture or corrosive substances such as acids and chemicals. They are widely used in many industries such as oil and gas production, chemical production facilities, and wastewater treatment facilities.
Furthermore, stainless steel tubing is extremely strong and resilient and can survive high-pressure settings like offshore structures, nuclear power plants, hydraulic systems, steam pipes, and nuclear reactors. Additionally, due to their great thermal conductivity, heat exchangers, which are widely employed in heating systems and industrial operations, can transport heat effectively.
Stainless steel tubes are very versatile. For example, as pipework and structural support in the construction industry, for exhaust systems in the automotive industry, for processing, storing, and transporting foodstuffs in the food and beverage industry, for aseptic environments in the pharmaceutical industry, and for sleek and modern aesthetics in the building industry.

Properties and Characteristics of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel stands out from other metals because of a variety of outstanding qualities. Excellent corrosion resistance is one of its distinguishing features.
Due to the presence of chromium in its composition, stainless steel forms a thin yet robust oxide layer on its surface when exposed to oxygen. Stainless steel is the material of choice for applications in hostile environments or when contact with moisture is unavoidable since this passive covering protects it from corrosive substances.
Stainless steel’s exceptional strength and endurance, which enable it to endure heavy loads and prevent deformation even in severe situations, are another notable characteristic.
This inherent strength makes stainless steel tubing very suitable for use in industries such as oil and gas pipelines or structural components subjected to high pressure. In addition, stainless steel has excellent heat resistance. It can withstand high temperatures without losing dimensional stability or structural integrity. Due to this property, stainless steel pipes are essential in settings where heat transfer or thermal insulation is important, such as in the chemical or power sectors.
Stainless steel is a prominent material that has revolutionized industries all over the world due to its superior corrosion resistance, durability, and heat resistance.

The Manufacturing Process of Stainless Steel Pipe
Raw Materials Used in Production
The quality and properties of the finished product can be significantly impacted by the careful choice of raw materials for stainless steel tubes.
Iron ore, chromium, nickel, and different alloying elements are the main ingredients utilized in the creation of stainless steel. Chromium increases stainless steel’s strength and adds corrosion resistance to the iron ore that serves as its basis material. Nickel enhances the overall stability of the alloy by increasing its ductility and high-temperature resistance. Alloying elements like molybdenum, titanium, and nitrogen can be added in precise proportions to further enhance specific properties based on the desired application of the stainless steel pipes.

Processes of Melting and Refining
Once the raw materials are collected, they undergo a melting and refining process to obtain the desired stainless steel alloy composition. One commonly used method is the electric arc furnace (EAF) method. In this process, scrap metal along with selected raw materials is charged into an electrically powered furnace. The intense heat generated by electric arcs melts these ingredients together to create a liquid-state alloy. Another widely employed method is known as the basic oxygen furnace (BOF) process.
In a converter tank walled with refractory material, molten iron produced in a blast furnace or recycled scrap metal is exposed to pure oxygen by being blown onto it. This procedure helps refine and purify the molten iron, producing high-quality stainless steel by oxidizing any impurities like carbon and silicon that are present.
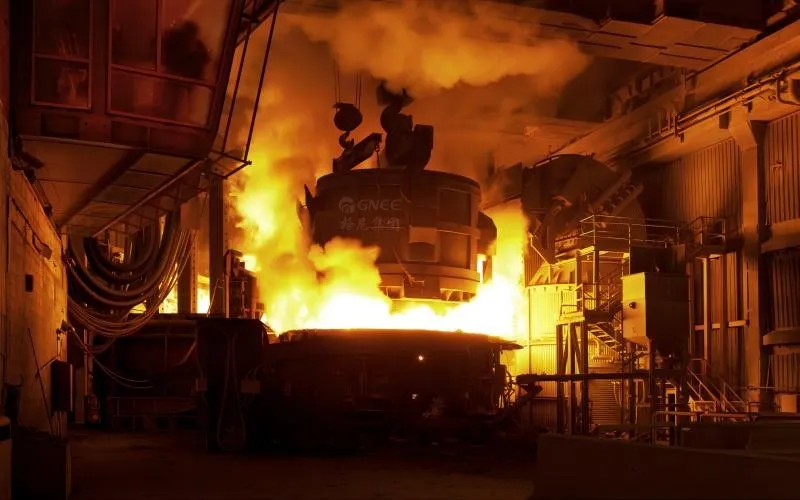

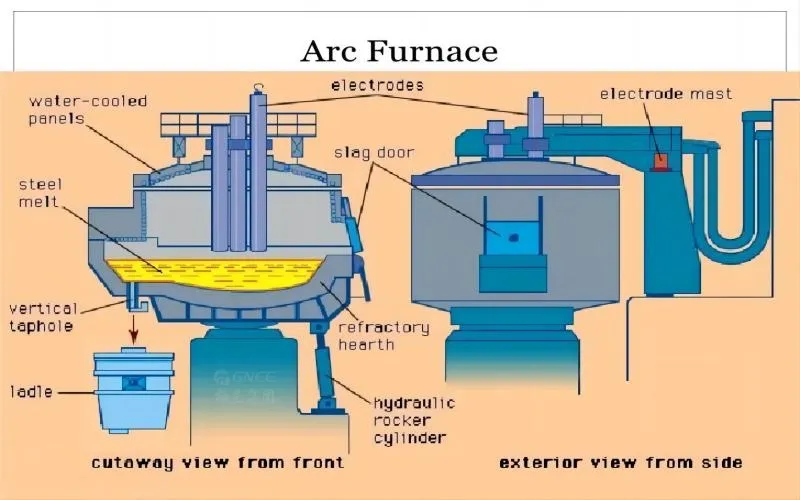
Electric Arc Furnace Method
One of the primary methods used for producing stainless steel is through electric arc furnaces (EAFs). These furnaces are made out of a sizable pot that is walled with heat-resistant bricks and can survive the high temperatures that are produced while they are in use. To heat the raw materials inside the furnace until they melt and combine into a homogeneous slurry, the EAF process uses strong electrodes to produce an electric arc.
Once the electrodes are lowered into the furnace, an electric current passes through them, producing immense heat that reaches temperatures above 3000 degrees Celsius. The basic materials are destroyed by the extreme heat, which also triggers a chemical reaction that produces a molten alloy of stainless steel.
The composition of the alloy can be precisely controlled by adjusting the proportions of different raw materials introduced into the furnace. Because of their adaptability, stainless steel pipes can be customized by manufacturers to fulfill unique industrial needs.
Basic Oxygen Furnace Method
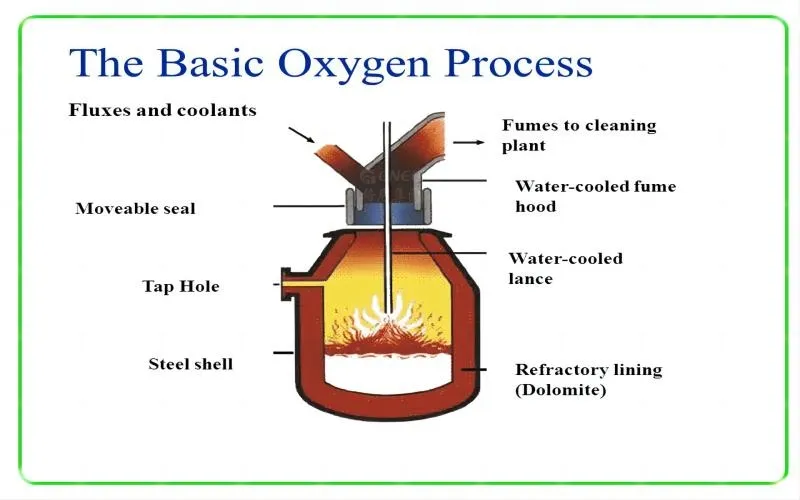
Another essential step in the manufacture of stainless steel is the basic oxygen furnace (BOF) procedure. In this method, molten iron produced from a blast furnace or scrap metal is transferred into a converter vessel lined with acidic refractory material. Pure oxygen is then blown onto the molten iron bath at high velocities, causing rapid oxidation of impurities present in the metal. As oxygen interacts with impurities like carbon and silicon, they undergo combustion reactions and are eliminated as carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide gases respectively.
The molten metal is kept at a high temperature during refining thanks to the exothermic reaction’s massive heat output. The process is continued until the required quantity of impurities has been removed from the molten iron, yielding refined stainless steel suitable for building pipes.
The quality, purity, and desirable qualities of stainless steel can be determined by using any of these two main procedures for melting and refining the metal. Manufacturers carefully select these processes based on factors such as cost-effectiveness, quality requirements, and desired alloy compositions to produce exceptional stainless steel pipes used across industries worldwide.
Different Stainless Steel Pipe Types
Seamless Stainless Steel Pipes
Hot-rolled Seamless Pipes
The efficiency and reliability of hot-rolled seamless tubes come to the fore when manufacturing stainless steel tubes. The production process begins with heating a solid cylindrical billet, usually made of stainless steel, to a temperature above its recrystallization point. It is then pierced through by a mandrel in a piercing mill to create a hollow tube. The tube is further elongated and reduced in diameter using multiple rolling stands until it reaches the desired dimensions and surface finish.
The advantages of hot-rolled seamless pipes are manifold. Firstly, they possess exceptional mechanical properties due to the absence of any welding seams or joints that can compromise integrity.
They are therefore suitable for use in demanding environments where reliability and longevity are essential. Industries such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and power generation heavily rely on hot-rolled seamless pipes for their resistance to internal pressure and ability to withstand harsh operating conditions.

Cold-drawn Seamless Pipes
For applications requiring exact dimensions and smooth surfaces, cold-drawn seamless steel tubing is a great option. Production processes include hot rolling stainless steel tubes, drawing, or broaching. In the drawing, the tubes are pulled through a die with a smaller diameter to reduce both outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness while improving surface quality.
On the other hand, filtering involves passing the tube through two or more rolls to achieve similar results. Cold-drawn seamless pipes exhibit several benefits over their counterparts produced by other methods. Firstly, they have superior dimensional accuracy with tight tolerances achieved during the cold-working process itself. They are appropriate for application in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and instrumentation thanks to their precision. Cold working also enhances the mechanical qualities of stainless steel while strengthening and hardening it.

Welded Stainless Steel Pipes
Electric Resistance Welding (ERW)
The process of producing stainless steel pipes known as electric resistance welding (ERW) is very popular. A flat strip or coil of stainless steel is sent through a succession of rollers to be formed into a cylindrical shape. The edges are then heated using an electric current and pressed together under pressure to create a solid weld seam. After welding, the excess material is trimmed and the pipe undergoes further sizing and straightening processes.
ERW pipes are excellent for a variety of applications due to their many benefits. Firstly, they can be produced in large volumes at a relatively low cost compared to seamless pipes. Additionally, good weld quality and uniform mechanical qualities are provided by ERW welding along the full length of the pipe.

Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) is another commonly employed method for manufacturing welded stainless steel pipes, particularly those with larger diameters. In this process, an arc is created between a continuously fed bare electrode and the workpiece while being submerged under a layer of granular flux material. The heat generated by the arc melts both the electrode and base metal, forming a molten pool that solidifies to create a welded joint. For big-diameter pipelines like water distribution networks or oil pipelines, SAW offers special benefits.
The process allows for high deposition rates with excellent weld quality due to its controlled environment free from atmospheric contamination. SAW is a cost-effective option for large-scale projects that call for vast lengths of welded stainless steel pipes because it is also very effective. These various stainless steel tube types can be used for applications requiring precision or high pressure in a variety of industries. Choosing the appropriate tube can be aided by being aware of their advantages and production methods.

Sanitary Stainless Steel Pipes
To guarantee the integrity of the goods and processes they are utilized in, these specialized pipes are created to adhere to rigid hygiene standards and production specifications.
Sanitary stainless steel pipes are crafted from high-quality stainless steel alloys that possess excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand rigorous cleaning procedures without degradation. These pipes are perfect for delivering sensitive materials like meals, beverages, or medicinal ingredients since their smooth inner surface finish reduces the possibility of contamination or bacterial growth. Their non-reactive qualities also stop any unintended changes in taste, odor, or chemical makeup during manufacturing or transportation.

Duplex Stainless Steel Pipes
Due to its special composition, which combines austenitic and ferrite phases, duplex stainless steel possesses exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and toughness.
Duplex stainless steel’s composition typically consists of around 50% austenite phase and 50% ferrite phase. These pipes have a high tensile strength and exceptional resistance to pitting corrosion brought on by chloride ions. Moreover, duplex stainless steel pipes offer better weldability than many other types of stainless steel due to their lower thermal expansion coefficient. This characteristic makes them highly suitable for fabrication processes involving welding or forming. Due to its improved durability and performance, duplex stainless steel is the material of choice for demanding applications where both strength and corrosion resistance are crucial. It represents a noteworthy advance in material technology.

As the development of stainless steel tubes proves, through continuous improvement, we can create a better future hand-in-hand with steel tubes.


