What are Stainless Steel Pipes?
One kind of pipe composed of a steel alloy including nickel and chromium is called stainless steel pipe. It is renowned for being robust, resistant to corrosion, and adaptable. Because of their special qualities, stainless steel pipes are utilized in a wide range of sectors and applications.
Stainless steel pipes are widely employed in a variety of industries and applications due to their versatility. They provide outstanding durability, temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance. The particulars of the application, like the temperature, the kind of fluid or gas being conveyed, and the environment, determine which stainless steel pipe is best.
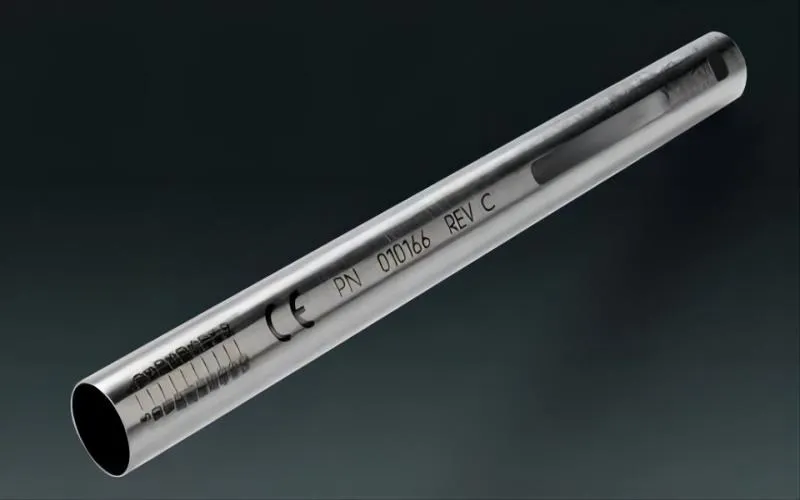

What is 304 Stainless Steel Pipe?
One particular kind of stainless steel pipe that is frequently utilized in many different sectors and applications is 304 stainless steel pipe. It is renowned for having outstanding formability, resistance to corrosion, and adaptability.
Important Facts Regarding 304 Stainless Steel Pipe:
Corrosion resistance: 304 stainless steel pipe has good resistance to corrosion from a variety of chemicals and from industrial environments.
Formability and weldability: It is extremely formable and quickly weldable using all standard techniques.
Certification: AMS-5639 and ASTM A276, A479 requirements are met by 304 stainless steel pipe, which holds dual certification.
Applications: Heat transfers, building supplies, chemical containers, kitchen appliances, and food processing equipment are among its frequent uses.

Install Process of 304 Stainless Steel Pipe
One of the primary components of industrial steel is the double carbon found in 304 stainless steel pipe. The amount and distribution of carbon in steel determine a lot of its characteristics and structure. In stainless steel, carbon has a particularly large impact. There are two primary ways that carbon affects the microstructure of stainless steel. On the one hand, carbon (about 30 times that of nickel) is an element that stabilizes austenite to a great extent. Contrarily, carbon has a strong attraction for chromium. As a result, the strength and corrosion resistance of stainless steel are contradicted by the carbon in the material.
In the process of installing stainless steel and bayonet grooves, precision in size, alignment, and lack of skewness are essential. The hardwood strips with fixed grooves are precisely sized, precisely shaped, and compliant with design specifications. To guarantee that there is a tight fit between the wooden strips and the stainless steel tank, the wooden strips have exact measurements. To prevent breaking the stainless steel tank during installation, forceful banging is not necessary. It can guarantee that there is no unevenness and that the stainless steel tank’s surface is consistent with the cylinder’s surface.
A firm binding is ensured, and the sides of the groove surface are prevented by the hardwood strips’ exact shape, ability to embed the stainless steel groove, and level bonding surface.
To ensure correct fitting and operation, there are multiple procedures involved in the installation process of 304 stainless steel pipe. An overview of the installation procedure is provided below:
1. Construction Preparation: It’s critical to set up the work site and collect all required equipment and supplies before beginning the installation.
2. Material Entry and Inspection: Make sure the 304 stainless steel pipes arrive at the location safely, and then examine them to look for any flaws or damage.
3. Cutting: Determine the pipes’ dimensions and mark them accordingly. To precisely cut the pipes, use the proper cutting instruments.
4. Production and Installation of Discharge Line and Hangers: To support the pipes, install the discharge line and hangers. It is recommended to space the hangers at regular intervals to give adequate support and avoid sagging.
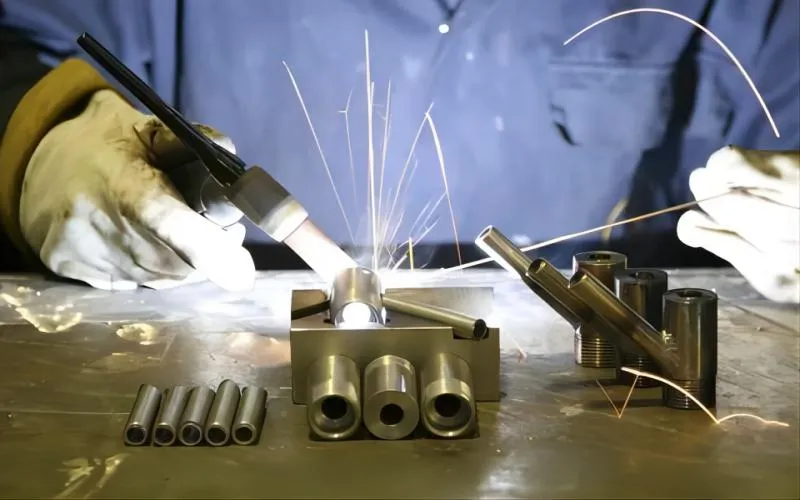
5. Welding: Use stainless steel-appropriate welding techniques to connect the pipes. To ensure sturdy and secure connections, make sure the welding is performed by a trained welder.
6. Pickling and Polishing the Welds: After welding, polish the welded joints to smooth out any sharp edges or flaws. You can also pickle to get rid of any scale or discoloration that came from the welding procedure.
7. Passivation: To improve the surface of stainless steel’s resistance to corrosion, passivation is applied. To get rid of any impurities and encourage the development of a protective oxide layer, the surface must be cleaned and a passivating solution applied.