A Brief Description and Application of Thin-Walled Stainless Steel Pipes
A type of piping material that has the benefits of high strength, corrosion resistance, and environmental protection is a thin-walled stainless steel pipe.
Thin-walled stainless steel pipe offers higher corrosion resistance, is lower in weight, and has a longer lifespan than conventional cast iron and galvanized steel pipe. Additionally, installing thin-walled stainless steel pipe is easy and convenient, and it doesn’t need specialized equipment or expertise, which can significantly lower installation costs.
Thin wall stainless steel pipe is frequently used in drainage engineering because of its high strength and ability to sustain high pressure. Additionally, it is extensively utilized in the sewage treatment industry. Pipes used in wastewater treatment must be able to withstand challenging environmental conditions and guard against corrosion and pollution. Due to the outstanding corrosion resistance of thin-walled stainless steel pipe, corrosion and pipeline damage can be successfully avoided. Additionally, because thin-walled stainless steel pipe does not produce any toxic materials and has outstanding environmental performance, it is frequently utilized in sewage treatment projects.
Additionally, stainless steel tubing with a thin wall is frequently utilized in the building industry. The pipe used in the construction industry must operate well in a fire and be able to tolerate high pressure and temperature changes. The needs of the construction industry can be met by thin wall stainless steel pipe due to its excellent high-temperature resistance and fire performance. Thin-walled stainless steel pipe also has strong environmental performance and aesthetics, which can give a building a feeling of high quality and grade.
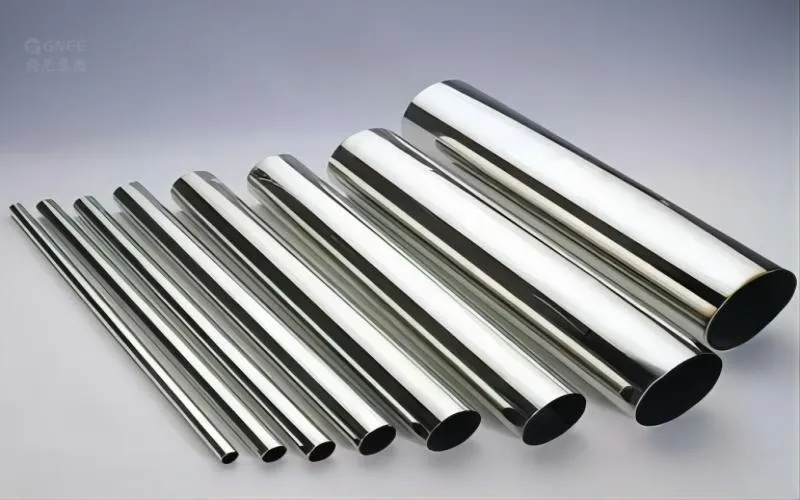

Some Common Models of Thin-Walled Stainless Steel Pipe
The most popular type is 304 stainless steel pipe, which is made of austenitic stainless steel with a chromium-nickel content of 18/8. They are light in weight and tiny in volume, and they have good strength and general corrosion resistance. Another popular variety is 316 stainless steel pipe, which has a strong resistance to chloride ion medium and is suitable for use in marine and seawater applications.
Thin-walled stainless steel pipes can be produced in a variety of dimensions and standards, with variations in their length, diameter, and wall thickness depending on the intended use. Depending on the needs of the application, the wall thickness ranges from 1mm to 30mm. In general corrosive applications, thin-walled stainless steel pipe is robust, corrosion-resistant, and lasts longer. For various application types, including seawater, marine, food processing, power generation, heat exchangers, oil and gas, and nuclear sector applications, several grades of thin-walled stainless steel pipes are readily accessible.
Thin-Walled Stainless Steel Pipe Connection Methods
1. Pressure Connection
“Single clamping” and “double clamping” are the two categories into which clamping types for thin-walled stainless steel pipes are separated. The connecting technique that is most stable is double clamping. To create the effect of a connection, the pipe fittings are clamped onto the pipe with hydraulic pliers, and the water is sealed with an O-ring. As a result, it is simple to use, effective at sealing, and impossible to deconstruct.
2. Flange Connection
Flange connections are made by tightening bolts to join two flanged connecting pipe fittings. Flat seals are used to seal the connection. This connection method is reasonably established, has a high pressure-bearing capacity and connection strength, and can also be disassembled. However, the price is rather hefty.
3. Grooved Connection
The expansion convex ring pipe and the stainless steel pipe fittings are axially compressed to create the grooved connection, and the connection effect is produced through the water stop of the conical sealing ring.
4. Socket Welding Connection
This is done so that the stainless steel pipe can be inserted into the pipe fitting and then extended in a circle for an argon arc welding connection, causing the stainless steel pipe fitting to self-melt into a single piece. As a result, the link is dependable and needs little upkeep. Although the connection sites of the stainless steel pipe fittings are extended by a water expansion process similar to the compression stainless steel pipe fittings during the manufacturing of socket welded stainless steel pipe fittings.
5. Welding Connection
Hot melt welding is used to create welded connections. Although the strength of this sort of connection is great, it is challenging to meet regulations for the gas protection of the on-site welding interface, which could shorten the pipeline’s useful life. The craftsmanship of the welder has a significant impact on the installation quality, which is challenging to ensure.
6. Threaded Connection
In other words, the inner and outer interfaces are tightened with tapered pipe threads while the stainless steel pipe fittings and stainless steel pipes are directly tightened like screws. It is stated that to swiftly and conveniently create the connection effect, they can also be tightened directly with bare hands. In general, thin-walled stainless steel pipes should not be used with the threaded bolt connection method.
Summary:
Although each of the aforementioned six connection techniques has pros and cons, the double compression connection is the one that is most frequently utilized for thin-walled stainless steel pipes. It is the most straightforward, reliable, and secure connecting technique.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thin-Walled Stainless Steel Pipe
Advantages:
1. Strong corrosion resistance: Thin-walled stainless steel pipes can be utilized in a range of hostile settings due to their strong corrosion resistance.
2. High aesthetics: Users can have a lovely visual experience thanks to the surface’s smoothness and noble texture.
3. Lightweight: less cumbersome to install and carry than other metal pipes.
4. Effective thermal insulation: Can prevent heat loss and increase energy usage effectiveness.
5. Environmental protection: recyclable, lessens environmental harm.
Disadvantages:
1. Weak impact resistance: vulnerable to collision and impact, which might result in damage.
2. It is ineffective in filtering away impurities and odors from the water, necessitating the use of water purification equipment.
3. Sensitive to temperature variations: The size and toughness of pipes will alter in high- or low-temperature situations.
4. High production cost: Thin-walled stainless steel pipes have a higher manufacturing cost as compared to other conventional pipe materials.
5. Strict installation standards: Construction must be completed following specifications, and there are criteria for the technical proficiency of installation personnel.


